Productivity Tools
August 14, 2025
Salesforce and SAP Integration: The Complete Guide to Streamlining Enterprise Data Flow
Integrating Salesforce and SAP has become a pivotal strategy for enterprises seeking unified customer and operational visibility. When done correctly, this integration eliminates data silos, improves decision-making speed, and elevates customer experience.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover why integrating Salesforce with SAP matters, how to implement it effectively, and practical best practices-perfect for enterprise technology leaders pursuing seamless digital transformation.
What Are SAP and Salesforce?
SAP is a leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) software used by businesses to manage financials, supply chain operations, procurement, logistics, and more. It serves as the digital core of many large organizations, helping streamline critical back-office functions and enabling large-scale automation.
Salesforce, on the other hand, is the world’s leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform. It helps businesses manage customer interactions across sales, service, marketing, and commerce. Known for its scalability and cloud-first approach, Salesforce enables teams to track leads, manage accounts, and optimize customer engagement in real time.
Why Salesforce and SAP Integration Matters
Large organizations frequently rely on SAP for finance, supply chain, and manufacturing operations, while Salesforce powers sales, service, and marketing efforts. Without integration, these systems operate in silos, resulting in disconnected customer profiles, duplicate data entry, and delayed business insights due to fragmented reporting.
Integrating them fosters a 360-degree customer view, automated transactional workflows, and real‑time business insights. These capabilities are essential for improving response times, personalization, and operational efficiency. When sales, customer service, and back-office teams operate from the same unified data source, collaboration improves dramatically, and so does customer satisfaction.
Moreover, as enterprises expand their digital transformation efforts, aligning front-office and back-office systems becomes critical. It reduces the risk of miscommunication and improves forecasting, which directly impacts revenue and resource planning. Organizations also gain better visibility into KPIs that span departments-such as customer lifetime value, churn rate, and order fulfillment timelines-allowing for more cohesive strategy execution.
Common Use Cases Driving the Integration
Salesforce-SAP integration enables organizations to eliminate redundancies and optimize operations across departments.
Bidirectional Account Synchronization
Customer data remains consistent across both platforms. When a new customer is created or updated in Salesforce, the corresponding changes reflect in SAP, and vice versa. This ensures everyone from sales to finance works with the same customer data, reducing errors and accelerating workflows.
Order-to-Cash Automation
Sales orders entered in Salesforce can be automatically converted into SAP process orders, with real-time updates on delivery and billing status flowing back into Salesforce. This streamlines sales operations, reduces manual data entry, and improves invoicing accuracy.
Real-Time Inventory Visibility
Sales reps gain access to accurate stock levels, leading to reliable customer commitments and better delivery estimates. Visibility into available-to-promise inventory helps prevent over-selling and enhances customer trust.
Enhanced Customer Support
Support agents benefit from integrated access to billing history, service contracts, and delivery information from SAP while managing cases in Salesforce. This context allows for quicker resolution and a better customer experience.
Integration Methods: Which Approach Fits Your Enterprise?
Choosing between iPaaS vs custom middleware depends on your integration goals, team expertise, and compliance requirements. iPaaS platforms offer faster deployment, while custom builds provide maximum control.
There are three primary approaches to integrating Salesforce and SAP:
Pre-built Middleware Platforms
Pre-built middleware platforms, often categorized as iPaaS (integration platform as a service), enable quick, low-code connectivity between Salesforce and SAP. Tools like MuleSoft’s Anypoint Platform, SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI), Dell Boomi, and APPSeCONNECT offer prebuilt connectors, data mapping templates, and real-time synchronization. These solutions streamline common integration scenarios such as account sync and order-to-cash automation. With built-in monitoring, error handling, and scalability, iPaaS platforms are ideal for enterprises seeking fast deployment without complex development.
Custom Integration
Custom integration is best suited for businesses with unique workflows or strict regulatory needs. This approach uses SAP IDocs, BAPIs, and Salesforce REST/SOAP APIs to build tailored sync flows and business logic. While it demands more technical expertise and longer implementation time, it provides maximum control over transformation, validation, and compliance. Custom methods are often chosen in industries like finance or manufacturing, where integration needs go beyond what standard platforms offer.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid integration combines pre-built middleware for standard data flows with custom logic for specialized use cases. This model allows teams to scale quickly while still supporting region-specific compliance, tax rules, or complex data transformations. It’s especially effective for enterprises running multiple SAP modules like S/4HANA or ECC and integrating with different Salesforce Clouds. A hybrid strategy balances flexibility and speed, making it a popular choice for global organizations with evolving integration needs.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices
Designing a successful Salesforce-SAP integration requires careful planning:
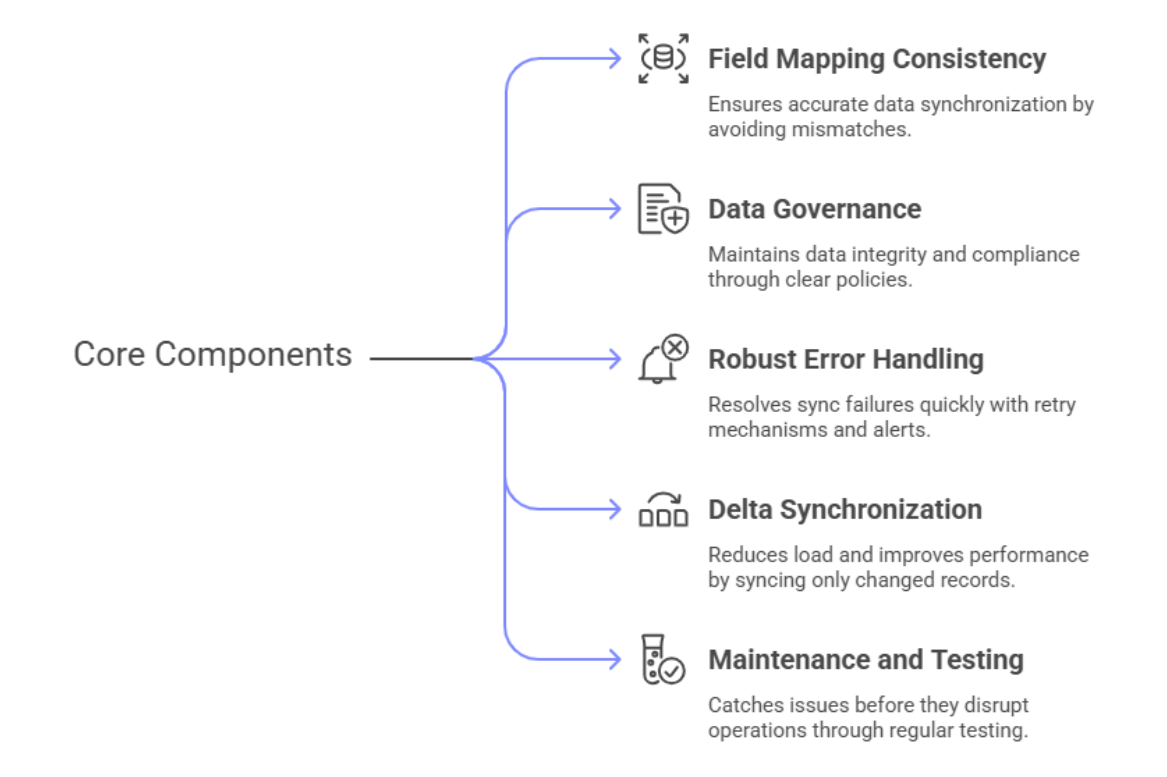
Salesforce-SAP integration infographic outlining best practices including field mapping, data policies, error management, delta sync, and testing processes for successful system integration.
Implementation Roadmap: Step-by-Step
- Discovery Phase: Audit current systems and identify workflows and data dependencies. Collaborate with business stakeholders to understand pain points and opportunities.
- Platform Selection: Choose the integration platform that aligns with your scale, cost expectations, and tech stack. Evaluate vendors based on reliability, support, scalability, and licensing models.
- Data Mapping and Transformation Design: Document schemas and transformation logic to handle data types, formats, and currencies. Pay attention to lookup tables, multilingual content, and validation rules.
- Development and Configuration: Build and configure the necessary sync flows, access controls, and security protocols. Ensure encryption for sensitive fields and establish API rate limit strategies.
- Testing and Validation: Simulate real-world use cases to ensure the system meets performance and accuracy standards. Include user acceptance testing (UAT) to validate functionality across departments.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Launch your integration in production with real-time monitoring and role-based governance. Use observability tools to track latency, throughput, and error frequency.
Summary and Benefits of Integration
Salesforce-SAP integration provides a unified view of customers and operations, enabling:
- Enhanced decision-making
- Automated order processing
- Real-time inventory updates
- Streamlined collaboration between departments
The integration supports better forecasting, compliance, and agility, helping businesses respond more effectively to market demands.
Additionally, organizations can leverage unified analytics to measure performance across the customer lifecycle-from marketing engagement to post-sale support. Integrated systems reduce operational costs by minimizing rework and eliminating redundant data entry.
Conclusion
Integrating Salesforce with SAP is a transformative strategy that drives operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. A successful integration requires strategic planning, the right tools, and a proactive approach to data governance.
As enterprises continue their digital journeys, integrating core systems like SAP and Salesforce becomes less of a luxury and more of a necessity. By unifying data, automating workflows, and enabling real-time insights, integration empowers companies to stay agile and competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Call to Action
Ready to streamline your operations with seamless Salesforce-SAP integration? Contact our experts for a personalized roadmap or explore our integration tools to get started.
FAQ
What is the difference between real-time and batch integration in Salesforce-SAP workflows?
Real-time integration syncs data instantly between Salesforce and SAP using event-driven APIs or middleware triggers, ideal for time-sensitive processes like order status updates or inventory availability. Batch integration, on the other hand, transfers data in scheduled intervals-often hourly or daily-making it better suited for high-volume, non-critical records like historical data migration or periodic financial updates.
Can I integrate SAP S/4HANA with Salesforce Service Cloud?
Yes. Both SAP S/4HANA and Salesforce Service Cloud can be connected using integration platforms like MuleSoft, SAP CPI, or Dell Boomi. These tools support workflows such as service contract syncing, billing visibility, and warranty management. Pre-built Salesforce SAP connectors often include templates to accelerate these integrations.
What are the most common challenges in Salesforce and SAP integration?
Typical challenges include inconsistent data formats, mismatched field mappings, API throttling, and sync latency. Errors often arise from SAP IDoc processing failures or misconfigured Salesforce APIs. Mitigating these issues requires clear data governance, sandbox testing, retry logic, and real-time monitoring dashboards.
How much does it cost to implement Salesforce SAP integration?
Integration costs can range from $50,000 to $200,000 or more depending on the complexity, number of systems/modules, and whether you choose a middleware-based or custom integration model. Licensing fees for tools like MuleSoft or SAP CPI and internal development resources also affect total cost of ownership (TCO).
How long does it take to integrate SAP and Salesforce?
Simple integrations using pre-built connectors can be completed in 3–4 months, while complex, multi-module deployments involving custom APIs may take 6–12 months. Factors like data volume, system customization, and stakeholder alignment influence the overall timeline.
Like what you see? Share with a friend.
Itay Guttman
Co-founder & CEO at Engini.io
With 11 years in SaaS, I've built MillionVerifier and SAAS First. Passionate about SaaS, data, and AI. Let's connect if you share the same drive for success!
Share with your community




.png)
Comments