Learn how to connect Microsoft Dataverse to Engini, enabling efficient integration of your business data and application logic. With the Dataverse connector, you can access structured data in real time, automate workflows, and unify information across different services. Effortlessly manage entities, relationships, and custom tables to support business processes and analytics.
To get started with the Microsoft Dataverse, create a free account at Microsoft or use your organizational Microsoft account.
Connecting Engini to Microsoft Dataverse #
- Enter your Engini account at https://app.engini.io.
- Navigate to Connections page by clicking on the Connections on the left side bar or by clicking here.
- Click on the “Add connection” option located at the top bar.
- Choose “MIcrosoft Dataverse” option from available applications.

- Enter the following details in the “Add Connection” form:
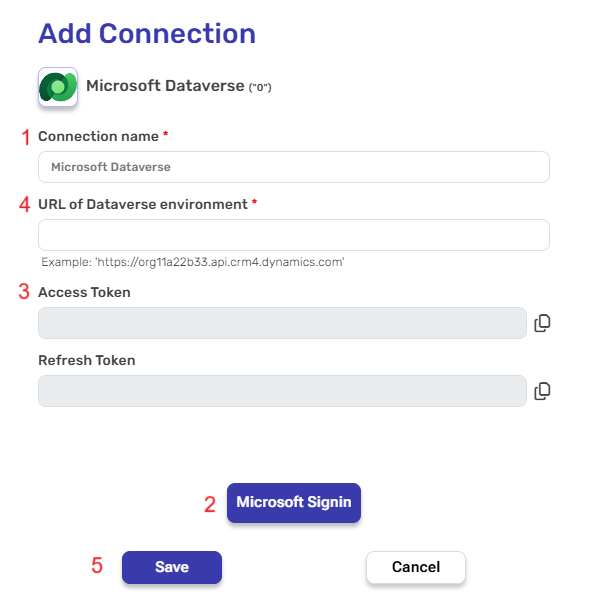
- Connection name – A unique identifier for the connection within Engini.
- Microsoft Signin – this is the authentication process where users log into their Microsoft account to gain access to Microsoft services.
- Click on the button to sign in to your Microsoft account.
- Access Token & Refresh Token – Automatically populated post connecting to a your Microsoft account.
- Access Token – A temporary security token that allows your application to access protected resources or APIs on behalf of the user. It serves as proof that the user has granted permission.
- Refresh Token– A token with an extended lifespan used to request a new Access Token once the original one expires, without requiring the user to log in again
- URL of Dataverse environment – The URL of a Dataverse environment is the web address you use to access your specific Dataverse workspace, where your data is stored and managed.
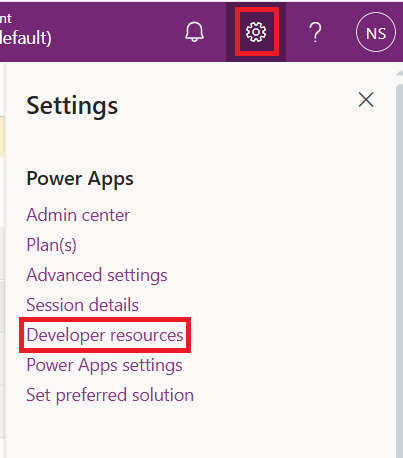
- To access this, sign in to your Microsoft Dataverse account and navigate to Settings
- In the opened menu, select Developer Resources.
Navigate to the section labeled ‘Web API Endpoint’ and copy the Base URL highlighted in the picture to in Engini.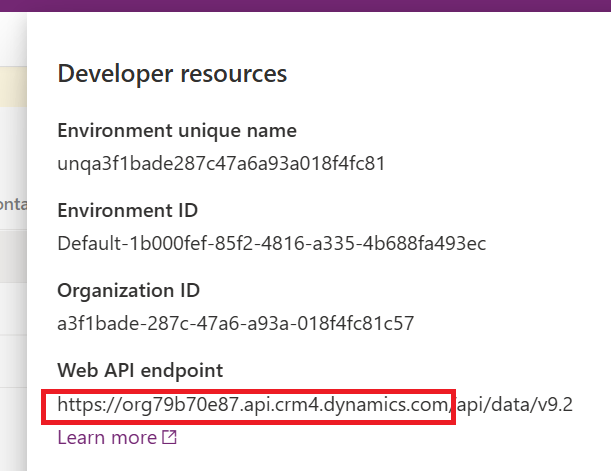
- Click on the save button to save the connection.
- After you’ve saved the connection, a window will open displaying all available entities and actions. From this window, select the entities and actions you want to use.
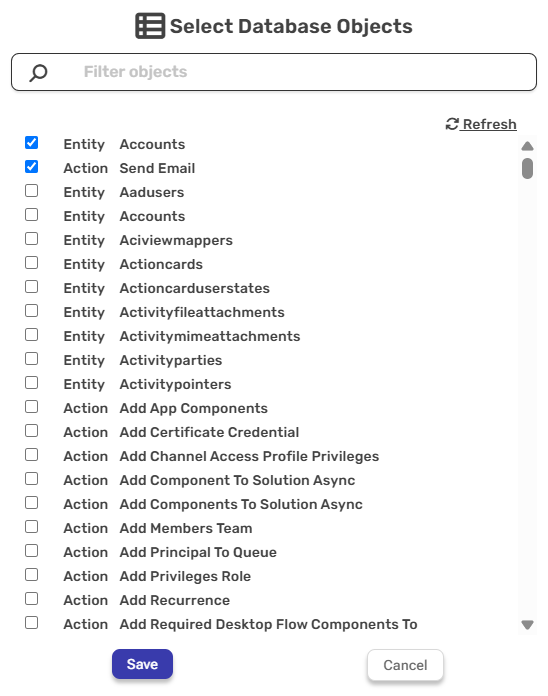
Once you’ve finished selecting the entities and the actions, click Save.
Note: After you’ve saved the connection, you can add additional objects and actions.
On the right side of the saved connection, you’ll see three dots.

- Click on the three dots and then click on “Select database objects”.
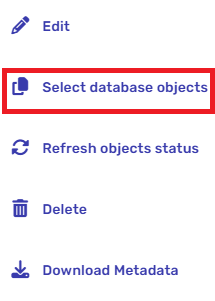
- A window will open displaying all available entities and actions, just like when you saved your connection. From this window, select the new entities and actions you want to use.

Once you’ve finished selecting the additional entities and actions, click Save.
Triggers #
Engini has one trigger for Microsoft Dataverse. This trigger is an automated trigger that activates when a specific event occurs on a Dataverse entity.
Entity Event Trigger #
Triggers when an event type is activated.
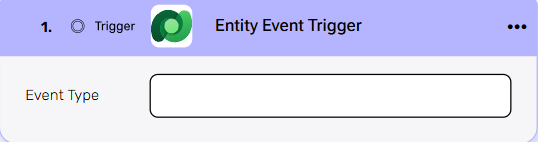
Event Type – Select the type of event that will trigger the workflow to start. Common event types include creation, update, or deletion.
Activities #
Create Record #
This activity creates a new record in Microsoft Dataverse based on yours selected object.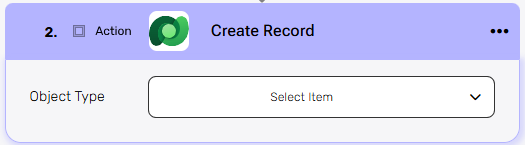
Object Type – Select the object you want to create (e.g., Accounts, Contacts).
After selecting a specific object, you will have the option to populate it’s fields by using “Add Field”.
Add Field
By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields in the record you are creating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.

- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Create Records Batch #
This action creates multiple new records in Microsoft Dataverse in one batch operation.
- Object Type – Select the type of object (table) where the records will be created.
- Data List – Provide the list of records to be created. Each item in the list should match the structure of the selected object type.
After selecting a specific object, you will have the option to populate it’s fields by using “Add Field”.
Add Field
By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields in the records you are creating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.

- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Delete Record #
This action deletes a specific record from Microsoft Dataverse based on the selected object type.
Object Type – Select the type of Microsoft Dataverse object you want to delete (e.g., Accounts, Contacts).
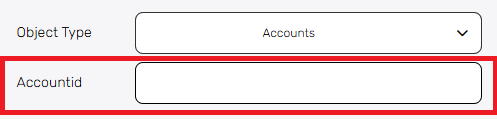
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the unique ID of the specific record you want to delete. For this object, it’s the Account ID.
Delete Records Batch #
This action removes multiple records from Microsoft Dataverse in a single batch operation.
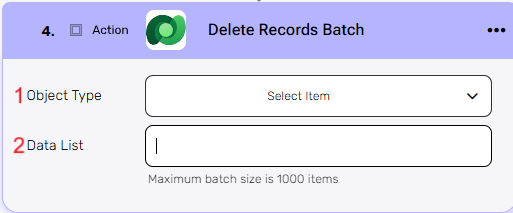
- Object Type – Select the type of object from which the records should be deleted.
- Data List – Provide the list of records to be deleted. Each item in the list should match the structure of the selected object type.
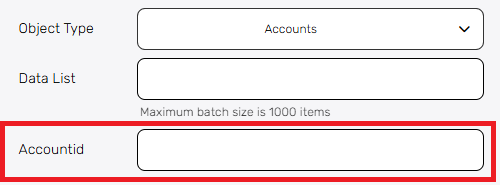
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the unique ID of the specific records you want to delete.
Execute Action #
This action executes an operation from the list you selected during the connection setup.
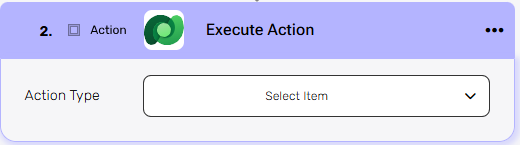
Action type –Click the dropdown and select the specific action to be performed from the list.
After selecting the action type (e.g., Send Email), provide the necessary details for the action.
- Issue Send – Define when or under what condition the email should be sent.
- Add Field – By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields for the action being executed. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.

- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Get Record #
This action retrieves a specific record from Microsoft Dataverse based on the selected object type.
Object Type – Select the type of Microsoft Dataverse object you want to retrieve (e.g., Accounts, Contacts).
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the necessary detail.
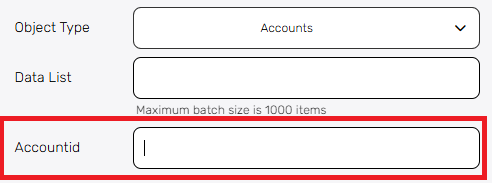
- Accountid – Provide the unique identifier of the record you want to retrieve.
- Output fields – Specify which fields you want to retrieve from the record.
Get Records #
This action retrieves multiple records from Microsoft Dataverse based on the selected object type. You can optionally apply filters, sorting, and set a limit (Top N) on how many records to fetch.
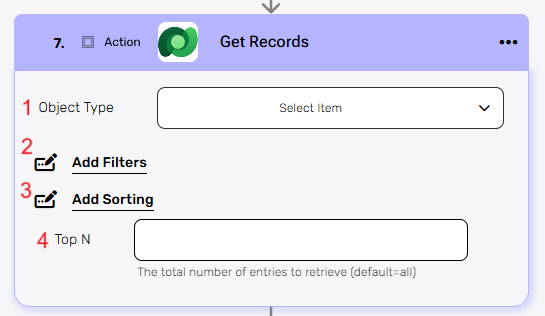
- Object Type – Select the type of object you want to retrieve records from.
- Add Filters – You can specify which records will be returned from the search results by utilizing the “Add Filter” button.
- Choose from the drop down the field you want to filter by.
- Select the condition you want the records to meet for the selected field.
- Click on the field to show the tooltip with all the options you can choose.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Add Sorting
You can define your own sort for the records.- Click on the “add sorting” button.
- Choose from the drop down the field you want to sort by.
- Choose the sorting option: descending or ascending.
- You can do a multi sort by choosing to sort more than one field. Use the arrows on the right to select the field that will be used as the primary sort, secondary, etc.
- Top N – You can specify how many records with the same value you want to get. Click on ‘Top N’ and enter the maximum number of values you want to retrieve.
If you setTop N = 1, a single record will be returned instead of an array. If no record is found, the action will fail, allowing you to implement an IF condition within the workflow. This can be useful for processes where the existence of a record determines the next steps in the workflow.
Get Records Batch #
The Get Records Batch action retrieves multiple records from Microsoft Dataverse in a single call based on a list of IDs.
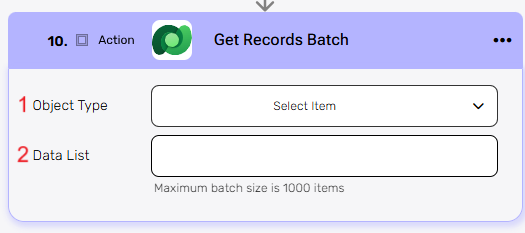
- Object Type – Select the type of object to retrieve records from.
- Data List – Provide the list of records to be retrived. Each item in the list should match the structure of the selected object type.
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the unique ID of the specific record you want to retrieve.
Update Record #
This action updates an existing record in Microsoft Dataverse. It allows you to change one or more fields within a specified object
Object Type – Select the type of object that contains the record you want to update.
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the necessary detail.
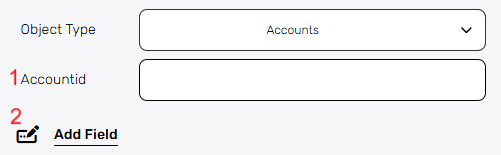
- Accountid – This field requires the unique identifier (ID) of the record you want to update.
- Add Field – By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields in the records you are updating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.

- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Update Records Batch #
This action updates multiple existing records in Microsoft Dataverse in one request.
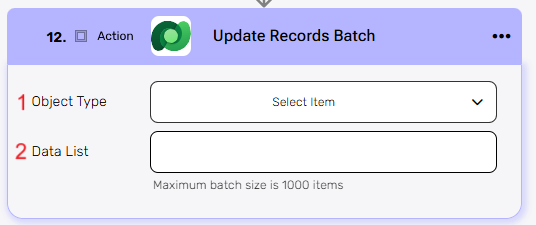
- Object Type – Select the type of object that contains the records you want to update.
- Data List – Provide a list of records to update.
After selecting the object type (e.g., Accounts), provide the necessary detail.
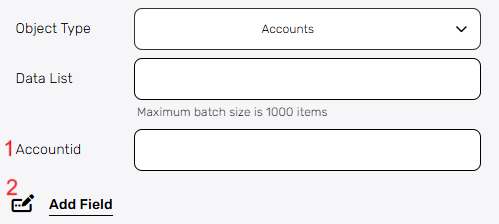
- Accountid – This field requires the unique identifier (ID) of the record you want to update.
- Add Field– By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields in the records you are updating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.

- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Initialize Object Array #
This action initializes an array variable that holds objects of the selected type.
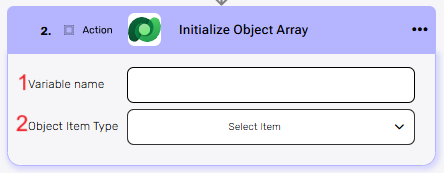
- Variable name – Enter a name for the array variable that will store the list of objects.
- Object Item Type – Select the type of object that each item in the array will represent.
After selecting a specific object item type, you will have the option to populate it’s fields by using “Add Field”.
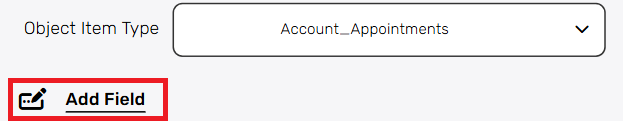
Add Field
By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields in the object you are creating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.
- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Append to Object Array #
This action adds a new object to an existing object array variable that was initialized earlier in the workflow.
Variable – Select the array you initialized in the previous steps.
After selecting the variable, the “Add Field” option becomes available.
Add Field
By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in various fields in the object you are creating. You can add one field to the activity or more fields to the activity definitions, up to the number of fields you have in the selected object. The fields vary depending on the selected object.
Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.
- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Map Object Array #
The map array activity allows you to transform a list of data items into a new data list based on the object’s properties and values you choose.
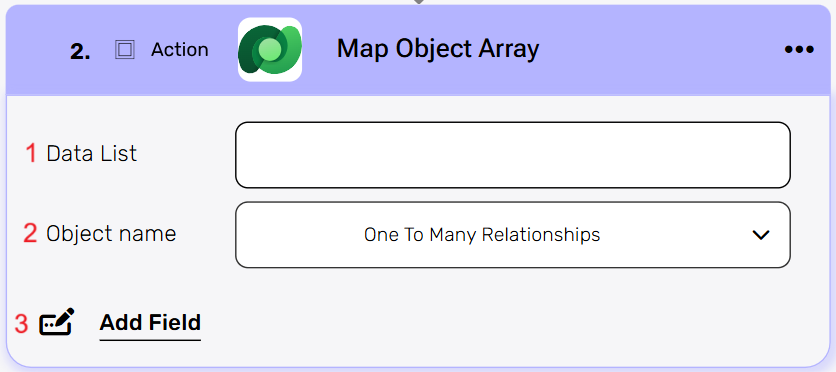
- Data List – Choose a data list that you’ve obtained from previous activities in your workflow. This data list typically contains an array of objects that you want to process and transform.
- Object name – Define the type of objects from the drop down that will be stored within the array.
- Add field– By clicking the “Add field” button, you can choose how to fill in the various fields when you are mapping.
- Choose from the drop down the field you want to fill.
- Click on the empty field to the right of the drop down to be shown the tooltip with all the options you can use to fill the field.
- You can populate the field in one of the following options:
- Static value – number / string. when using strings, you need to surround them with single quotes (‘).
- Property value from a previous activity (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Expression – using functions and/or Previous activity properties and/or static values (Using the tooltip that opens when clicking on the field).
- Repeat steps 1-3 for all the fields you want to populate.
Send Api Request #
This action allows you to send a custom API request directly to the Microsoft Dataverse API.
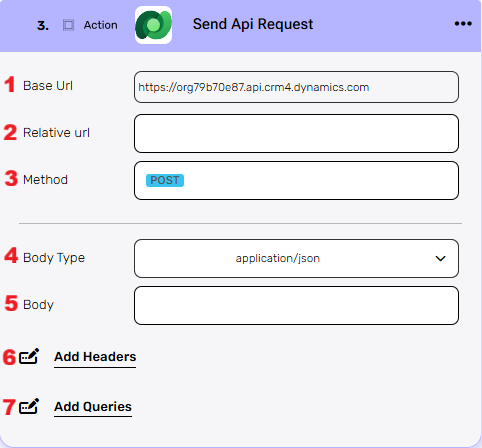
- Base Url – This is the root URL of the API you’re sending the request to.
- Relative Url – You can specify additional path segments or parameters that need to be added to the end of the automatically generated URL. This allows you to customize the specific request you want to perform.
- Method – Select the HTTP method (e.g., Get, Post, Put, Delete, Patch).
- Body Type – Defines the format of the data in the body of your request. A commonly used value is application/json , which means the body will contain a JSON-formatted payload.
- Body – Contains any data that is being sent to the server.
- Add Headers – Additional metadata about the request, such as the type of data that Engini can accept, the length of the request body, and authentication information.
- Click on the “Add Headers” button to add a header.
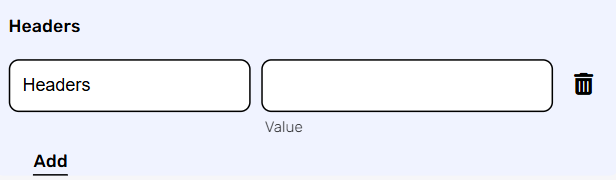
- Click on the headers field to enter the key, and on the value field to enter a value. Each header consists of a key-value pair, where the key is the name of the parameter, and the value is the data associated with that parameter.
- Click on the “Add” button to add more Headers.
- Click on the “Add Headers” button to add a header.
- Add Queries – The query refers to the parameters or data that are included in the URL of an HTTP request to provide additional information or instructions to the server.
- Click on the “Add Queries” button to add a header.
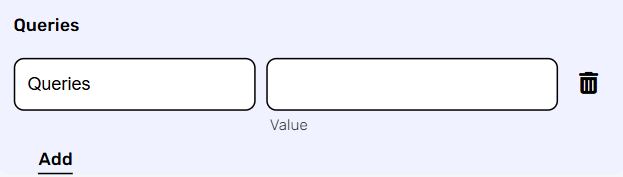
- Click on the queries field to enter the key, and on the value field to enter a value.
Each query consists of a key-value pair, where the key is the name of the parameter, and the value is the data associated with that parameter. - Click on the “Add” button to add more queries.
- Click on the “Add Queries” button to add a header.





.png)